What is Epigenetics?
Put simply, epigenetics is the study of mechanisms that switch on or off our genes. These mechanisms are hugely influenced by our environment, the food we eat and the toxins we are exposed to. We also need to look to the health of the parents, the health of their egg and seed at conception, the mother’s health during pregnancy and what environment the foetus is exposed to in utero.
According to whatisepigenetics.com, these mechanisms are involved in every aspect of life and such reversible changes are potentially heritable. Not only will they affect the way we live but also how our future generations live.
More specifically, research shows that maternal nutrient status during pregnancy can strongly influence the child’s long term future health. Poor nutrient status can mean a higher risk of developing illnesses such as high blood pressure and diabetes later in life. Adverse experiences early in life can also create non-desirable epigenetic modifications. Whereas, eating a Mediterranean Diet in pregnancy, might epigenetically protect the fetus from developing diseases later in life . These modifications can also pass on to the next generation to affect the child’s child. Therefore it is important to pay attention to the concept of the First 1000 Days.
The First 1000 Days.
The first 1000 days refers to the time between conception and baby’s second birthday. In recent years, science on early childhood development has shown how nutrition, environment and relationships can all hugely shape the future outcome of the baby’s physical and mental well-being. How well they do in school and how they prosper long-term impacts the economic status of their family and society. The consequences can be far-reaching.
Therefore, parents have a serious responsibility to firstly, properly nourish themselves to optimise fertility in preparation for conception. It is pertinent to note here, that the male’s contribution is equally significant. The health of the sperm plays just as an important a role in fertility and growing a healthy baby! Secondly, for the expectant Mum to nourish herself while pregnant. Thirdly, as an extension to this, it is important to talk about nourishment in post pregnancy for Mum and baby.
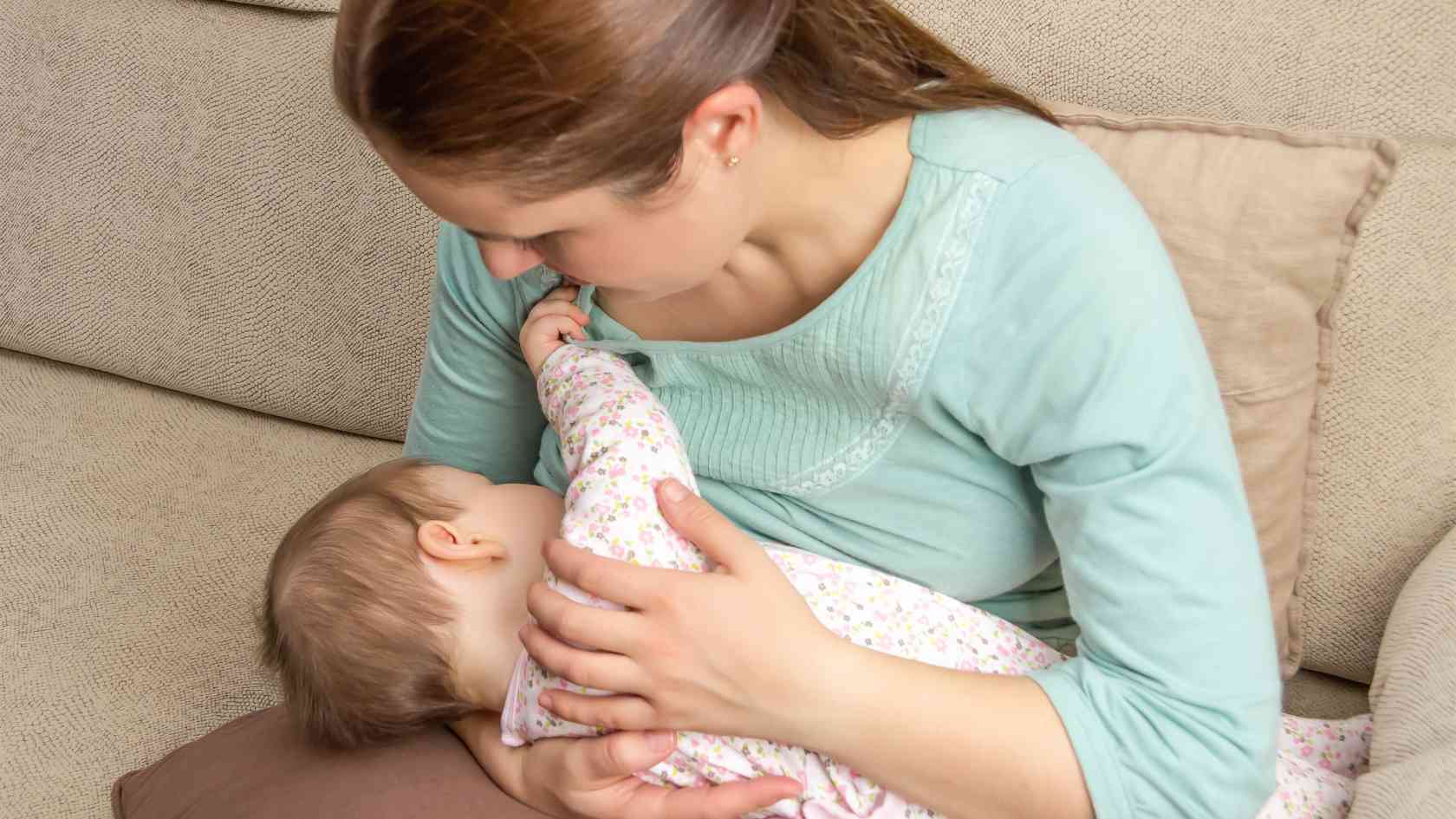

Fourth Trimester and Benefits of Breastfeeding.
Nourishment from food but also nourishing the body and brain through loving secure connections. This is vital for the child to develop the ability to feel empathy. One of the first ways a baby connects is through loving touch and smiles. The first and most natural way for Mum and baby to establish this is through breastfeeding. This benefits the psychological health of baby AND Mum. Breastfeeding stimulates the release of the hormone and neurotransmitter, oxytocin. Oxytocin helps to lower levels of stress and anxiety while also promoting feelings of warmth, trust and bonding.
Breast milk is also providing THE perfect balanced nutrition that the baby needs at this stage in life. It provides the ideal proportions of vitamins, minerals, protein and healthy fats. What may be compromised are levels of vitamin D. Health authorities recommend supplementing all babies with extra vitamin D for 1-2 years. Breast milk contains antibodies with high amounts of IgA. These antibodies are produced by the Mum in response to bacteria or viruses. They are passed to the baby through breast milk. As a result, the baby is then protected. Quite simply, mother produces what the baby needs within their environment and during that time.
This is something impossible for formula companies to replicate. It is well established that formula fed babies are at a higher risk of developing compromised respiratory health, ear and chest infections as well as susceptibilities to other illnesses. Where Mum cannot breastfeed it is important to ensure plenty of skin to skin contact between newborn and their caretakers, with plenty of loving gazes while bottle feeding!

Nurturing the Microbiome for Robust Immunity.
Another important area to consider is the baby’s gut flora to support long term resilience. Research is showing that the bacterial microbiota could influence gene expression. A health concern, relating to a lack of exposure to healthy gut bugs early in life, is the rise in atopic allergies in children today. It is estimated that by 2025 more than half of the EU population will be allergic. The baby’s first exposure to the micro flora is not at birth as originally believed, but in utero. Supporting a healthy gut and vaginal flora for the mother is vital to establishing a healthy microbiome for baby. This is supported through the mother’s diet and environment during pregnancy, through a natural birth and through breastfeeding. If for any reason any of these are compromised, it is important to pay attention to ways to counteract the effects.
In our exciting new CPD approved short course Smart Eating for Fertility & Pregnancy: A Nutrition & Lifestyle Guide, we provide trustworthy knowledge, insights and practical information to support the key stages in creating new life and bringing into the world a child primed and nurtured for a lifetime of robust good health.











